Antigens Can Be Made From Which of the Following Molecules
A Detecting these soluble molecules may help in the management of disease. The autologous or self-molecules are ordinarily not immunogenic but under certain circumstances these may act as antigens.

Antigen Definition Function Types Facts Britannica
An epitope is a molecular surface feature of.

. Two proteins hemagglutinin and neuraminidase on the surface of influenza viruses contain the major antigens targeted by antibodies see Figure 1. Route of Administration of the antigen eg. Haptens are usually small molecules eg.
1 a cell wall protein 2 a piece of DNA inside a cell 3 a protein that is part of a flagella 4 a uniquely shaped protein that is part of a virus 5 a protein that is only made by prokaryotic cells. An example is the alloantigen which is the antigen present in non-identical individuals of the same species eg. B In normal individuals the concentration of these molecules in serum is always low.
Various types of antigens present in the environment are pollens dust grains husk powders chemical agents foams etc. 4 Antigens are recognized by antigen receptors including antibodies and T-cell receptors. Exhibit foreignness recognized as non-self by the body.
Be of high molecular weight exhibit chemical complexity and. A The body has billions of genes for antigen receptors. E They may be natural or man-made molecules.
Most nucleated cells can be induced to express class II MHC molecules by interferon IFN-gamma. On the basis of the immune response antigens can be classified as. Page 820 Specific Resistance.
View the full answer. An antigen-presenting cell presents antigen to a helper T cell on its surface using ______. Which of the following molecules can serve as antigens.
Class II MHC molecules are usually present only on professional antigen-presenting cells B cells macrophages dendritic cells Langerhans cells thymic epithelium and activated but not resting T cells. These are non-protein foreign substances that require a carrier molecule to induce an immune response. Some of the other enzymes involved in the earlier stages of ABO antigen synthesis are also involved in producing antigens of the Hh blood group and the Lewis blood group.
Protein polysaccharides nucleic acids lipids. While both can bind to receptors antigen cannot induce immune response on its own whereas an immunogen can. Epitope of the antigen molecule may be destroyed if given orally.
Class I MHC molecules primarily present peptide products that are synthesized inside of the cell to cytotoxic CD8 T cells. The immune system responds more swiftly by making antibodies to an antigen after the first exposure because. Cell-associated differentiation antigens CDs are functional cell surface proteins or receptors that can be measured in situ.
The preimmune repertoire is. Moreover the antigen-binding sites of many antibodies can cross-react with a variety of related but different antigenic determinants making the antibody defense force even more formidable. Antigens are molecular structures on the surface of viruses that are recognized by the immune system and are capable of triggering one kind of immune response known as antibody production.
You may choose more than one. Which of the following molecules do you think would make good antigens for recognizing a pathogen. Which molecules make the best immunogen.
Protein is the best. Antigens can be proteins peptides amino acid chains polysaccharides chains of monosaccharidessimple sugars lipids or nucleic acids. Up to 24 cash back 7.
Lens protein and thyroglobulin may act as. Proteins nucleoproteins polysaccharides and glycolipids Which of the following statements about the acquisition of immunity is correct. MHC molecules then carry the antigen to the plasma membrane and form a complex that can be recognized by T cells.
Each MHC molecule can bind to various peptides and present those antigens to T cells. A helper T cell must be activated before it can stimulate a B cell to produce antibody. It has antigen from the disease-causing microbe on its surface.
Make sure to discuss the roles of the following molecules in your answer. 100 1 rating Antigen is defined as any biologicalnon-biological entity which can elicit an immune response in the host such as humans. Immunity Level of Difficulty.
Medium 25 Why can the body recognize so many different antigens. Chemically antigens are large molecular weight proteins including conjugated proteins such as glycoproteins lipoproteins and nucleoproteins and polysaccharides including lipopolysaccharides. Even in the absence of antigen stimulation a human can probably make more than 1012 different antibody moleculesits preimmune antibody repertoire.
Previous question Next question. After a B cell is activated to form plasma cells those plasma cells each produce different antibodies. Cytotoxic T-cells know that a cell is infected because.
Lipids and nucleic acids can combine with those molecules to form more complex antigens like lipopolysaccharide a potent bacterial toxin. Class II MHC molecules consist of 2 polypeptide alpha α and beta β chains. These antigens are incorporated into one of four types of oligosaccharide chain type 2 being the most common in the antigen-carrying molecules in RBC membranes.
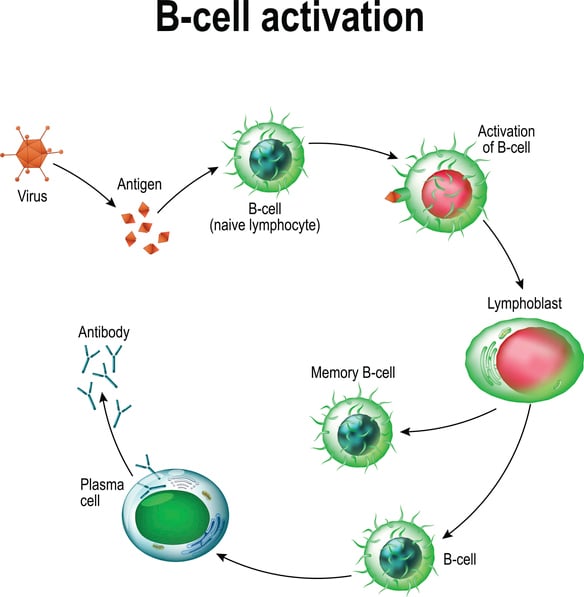
B-cells differentiate into ______ which make antibodies. Antigens are typically proteins peptides or polysaccharides. Genetic Makeup of the Host.
These may be proteins or polysaccharides and can generate an immune response on their own. HTML Editora Β Ι Ο Α - Α Ix E1 X X TTT 12pt Paragra Outline how an effector helper T cell causes a B cell to become activated. Toll-like receptor co-stimmulatory molecule co-stimmulatory molecule receptor MHC-II T cell receptor CD4.
B A given antigen receptor can bind many very different antigens.

Immune System Antigens Britannica
No comments for "Antigens Can Be Made From Which of the Following Molecules"
Post a Comment